The PIA, Nigeria’s loss of Over 2 Billion USD to Dwindling oil production in June 2022 and the Power of Voices Partnership (PVP) solution
Kingsley Agu (Programs Manager, CODE)
It is no longer news that the Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) is now transiting into a private company now known as Nigerian National Petroleum Company Limited (NNPC Ltd). NNPC Ltd is to be regulated in line with the provisions of the Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA) and the title of the former Group Managing Director (GMD) of the NNPC would now become Group Chief Executive Officer (GCEO) of the new NNPC Ltd (which means the GCEO has the powers to make decisions for its subsidiaries and holding company unlike before that it had to be via the Federal Executive Council). The new look NNPC Ltd is all as a result of the Section 53(1) of the Petroleum Industry Act (PIA) 2021 which mandated the Minister of Petroleum to incorporate NNPC Ltd within 6 months of the signing of the Petroleum Industry Act (PIA) 2021 into law. The PIA 2021 was signed into law by President Muhammadu Buhari on the 16th of August 2021 upon passage by the National Assembly in July 2021.
The NNPC Limited is currently the company with the highest share capital in Nigeria with 200 Billion Naira initial capital. The incorporation of the NNPC Ltd by Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) was concluded within 1 month and 5 days from the date the President signed the PIA 2021 into law as this was completed on the 21st of September 2021 by CAC. NNPC Limited is expected to be unveiled by President Muhammadu Buhari on 19th July, 2022.
Despite the current efforts at making NNPC to function optimally in line with the PIA 2021, crude oil production has been on a steady decline year-on-year from 2020 to 2022 half year. Available data from the Nigerian Upstream Petroleum Regulatory Commission (NUPRC) a subsidiary of the new CAMA incorporated NNPC Limited shows this worrying trend.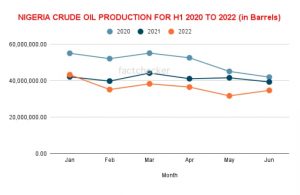
The data analysis above of Nigerian crude oil production for January to June 2020 to 2022 shows a consistent and worrying decline in oil production. In January 2022, the data shows a 11,795,487 Million Barrel drop in oil production of 43,353,723 Million Barrels in January 2022 when compared to January 2020 which was 55,149,210 Million Barrels. In February 2022, the data shows a 16,963,273.53 Million Barrel drop in oil production of 35,217,997.47 Million Barrels in January 2022 when compared to January 2020 which was 52,181,271 Million Barrels. This downward trend is visible across January to June as seen in the graphical representation of the analysis above.
The 2022 first half crude oil production performance shows a decline of 11.8% when compared to June of 2021 production. In June 2021, Nigeria produced 39,401,749 Million Barrels of crude oil while in June 2022, the production was pegged at 34,748,214. The graph below shows data visualization of the downward trend of oil production in 2022 when compared year on year with 2021. Though the data also shows an improvement in crude oil production in June 2022 when compared to the previous month of May 2022.
This is amidst dwindling foreign reserves and revenue shortfall in the country. This worrying trend has to be addressed else Nigeria might be in a more serious revenue crisis which might affect the functioning of the Nigerian government as crude oil still remains the major source of foreign exchange in the country. To visualize the extent of the revenue crisis due to oil production decline, out of the 1.772 Million Barrels per day (bpd) of crude oil production allocated to Nigeria by the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) in June 2022, Nigeria was only able to produce 1,158,273.80 Million bpd leaving a shortfall of 613,726.2 bpd which if calculated based on the $110 per barrel oil was sold for in June 2022, amounts to 67,509,882 Million US$ loss per day and as much as 2,025,296,460 Billion US$ loss in the whole of June 2022.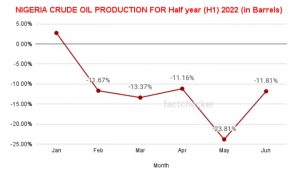
The decline in oil production is largely attributed to oil bunkering activities in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria, oil theft as well as decaying oil infrastructure. The oil bunkering activities in the Niger Delta is fueled by degraded environment due to crude oil activities thereby destroying the livelihood of community members in oil-producing communities who are predominantly crop farmers and fishermen/women as well as long years of neglect by successive governments which is evidenced by poor social infrastructures such as roads, schools, WASH and healthcare facilities despite the 13% oil derivative given to oil producing states by the Federal government of Nigeria.
To address this social misnomer across oil producing communities, Connected Development (CODE), Africa’s leading civil society organization, through its Power of Voice Partnership (PVP) Fair for All Campaign has via its collaborative intervention and advocacy worked with other CSOs including government agencies, resulting in the passage of the Petroleum Industry Act (PIA) with support from OXFAM.
The Act has well spelt out provisions for the establishment of the Host Community Development Trust to provide organized funding for development of oil producing communities and mitigate the risk of high conflict and restiveness in the areas and #RevampNigerDelta. Our specific engagements built the capacity of CSOs, community leaders and young people to be able to engage the private sector, oil and gas companies and the government and demand a participatory open budget and contracting system.
In the second phase of the PVP campaign, CODE will continue this engagement by giving attention to the implementation of the provisions of the newly enacted regulatory framework in the petroleum industry (Petroleum Industry Act). CODE will ensure that the government sustains the already created “Commission” and the “Authority” via the transition of NNPC to become a commercial entity with no regulatory powers as NNPC Limited. At the Community level, we will strive to track and monitor the implementation of the Host Community Development Trust. To address the gap in access to information by citizens in states where the Freedom of Information Act has not been domesticated, we will carry out advocacy drives to stimulate citizens to push for the domestication of the Act at the focal states of Delta, Akwa Ibom, Cross River, Imo, Rivers and FCT Abuja. For sustainability, we will also improve the capacity of CSOs to conduct evidence-based tracking and advocacy using the FollowTheMoney model to ensure effective utilization of resources in oil-producing states in Nigeria.




